4.3 KiB
Input node
Use an Input node to control the flow of logic and data from a Script Graph's Subgraph node. An Input node takes data from a parent graph and makes it available to a Subgraph.
For more information on Subgraphs, see Subgraphs and State Units and Subgraph node. For more information on Script Graphs, see Graphs.
Fuzzy finder category
The Input node is in the Nesting category in the fuzzy finder.
Available outputs
By default, an Input node has no ports.
An Input node can only have output ports. Define the number and specific data type for the output ports with the Graph Inspector. For more information on how to define ports on a Script Graph, see Add a Trigger or Data port to a Script Graph.
| Port Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Trigger Input | A control port. Make a connection to this port to tell Visual Scripting what node to run next in the graph. Visual Scripting triggers any node to this port after the matching Trigger Input port triggers on the Subgraph node in the parent Script Graph. |
| Data Input | A data port. Make a connection to this port to send a value or other data to another node in the graph. The data source is the matching Data Input port on the Subgraph node in a parent Script Graph. |
Example graph usage
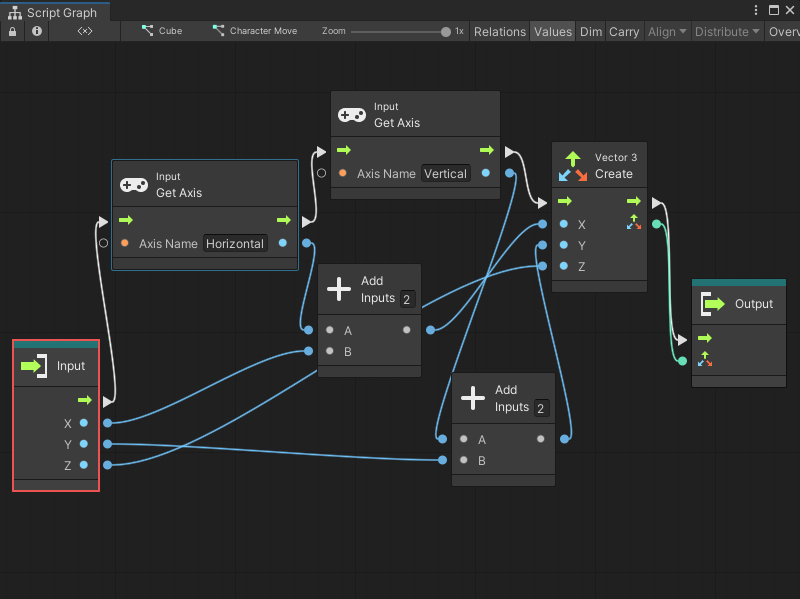
In the following example, the Character Move Subgraph uses an Input node to receive data from a parent graph. The Input node has one Trigger Input port and three Data Input ports. It uses the values from the parent graph and the values from two Input Get Axis nodes to create a new Vector 3 value that it sends back to its parent graph.
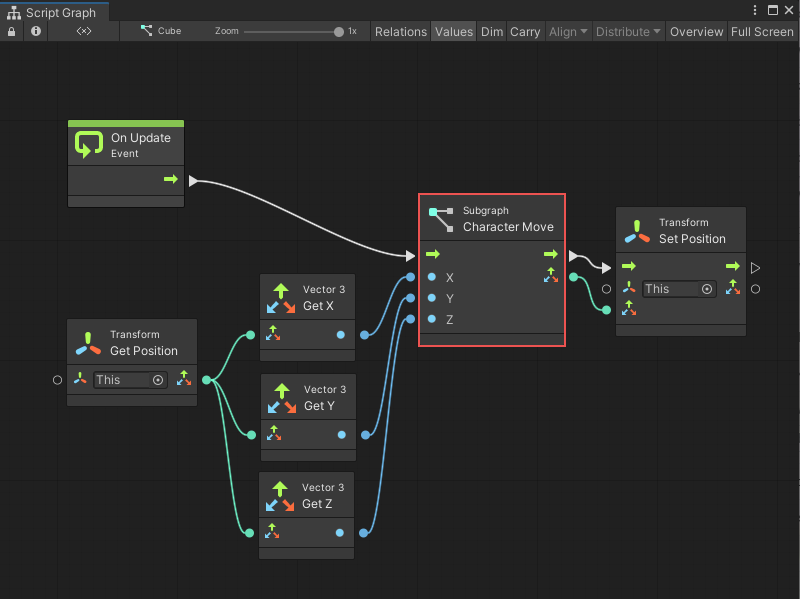
The parent graph sends three values from the current GameObject's Transform component to the Input node. The Subgraph reduces the number of nodes in the parent graph.
Related nodes
Use an Input node with the following nodes: